线性偏振
跳转到导航
跳转到搜索
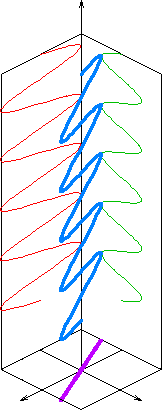
在电动力学中,電磁輻射的线性偏振或平面偏振是指电场矢量或磁场矢量在传播方向上被限制在某一固定平面内的现象。术语“线性偏振”(法语:polarisation rectiligne)由奥古斯丁·菲涅耳于1822年提出。[1]更多信息可参见偏振和偏振平面。
线性偏振电磁波的取向由電場矢量的方向定义。[2]例如,如果电场矢量是垂直的(随着波的传播交替上下),则称该辐射为垂直偏振。
数学描述
電磁波方程式中電場和磁場的經典正弦平面波解为(cgs单位制):
对于磁场,其中的是波數,
是x−y平面中的琼斯矢量。
当相位角相等时,即
- 。
这表示波相对于x轴以角度偏振。此时,琼斯矢量可写为:
- 。
x或y方向的线性偏振态矢量是此态矢量的特例。
如果定义单位矢量:
以及
则偏振态可以在“x−y基”下写为:
- 。
参考
- ↑ A. Fresnel, "Mémoire sur la double réfraction que les rayons lumineux éprouvent en traversant les aiguilles de cristal de roche suivant les directions parallèles à l'axe", read 9 December 1822; printed in H. de Senarmont, E. Verdet, and L. Fresnel (eds.), Oeuvres complètes d'Augustin Fresnel, vol. 1 (1866), pp.Template:Nnbsp731–51; translated as "Memoir on the double refraction that light rays undergo in traversing the needles of quartz in the directions parallel to the axis", Template:Zenodo, 2021 (open access); §9.
- ↑ Template:Cite book