
没有更高的分辨率。
本文件来自维基共享资源并可能被其他项目使用。
其文件描述页上的描述显示在下面。
摘要
Birkeland-Eyde style plasma disc. Two water-cooled copper tube electrodes are connected to a high voltage alternating current supply (connections and power supply are not shown) to produce a spark gap. Water circulates through the tubes to keep them cool as shown by the arrows. Direct current is applied to the electromagnet.
The arc starts between the electrodes and moves outward forming a semicircle due to the Lorentz force applied by the static magnetic field. Once the arc length becomes too long, a new one forms in the center between the electrodes and the process begins again. The direction the arc moves depends on the polarity. A high voltage alternating current results in a plasma disc, but pulsed DC results in a half disc.
Based on diagrams and description from the book "The Fixation of Atmospheric Nitrogen"[1] and a photo of the electrodes:
许可协议
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse
|

|
我,本作品著作权人,释出本作品至公有领域。这适用于全世界。
在一些国家这可能不合法;如果是这样的话,那么:
我无条件地授予任何人以任何目的使用本作品的权利,除非这些条件是法律规定所必需的。
|
- ↑ Knox, Joseph (1914年) 《 The Fixation of Atmospheric Nitrogen》、D. Van Nostrand Company、pp. 45−50
文件历史
点击某个日期/时间查看对应时刻的文件。
| 日期/时间 | 缩略图 | 大小 | 用户 | 备注 |
|---|
| 当前 | 2019年12月24日 (二) 02:02 | 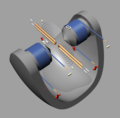 | 595 × 584(161 KB) | wikimediacommons>TreeOfKnowledge | Reshape the electromagnet to more closely resemble that of a Birkeland-Eyde reactor |
文件用途


